Advanced Laparoscopic Hernia Treatment
Hernia
What is Hernia?
How does it form?
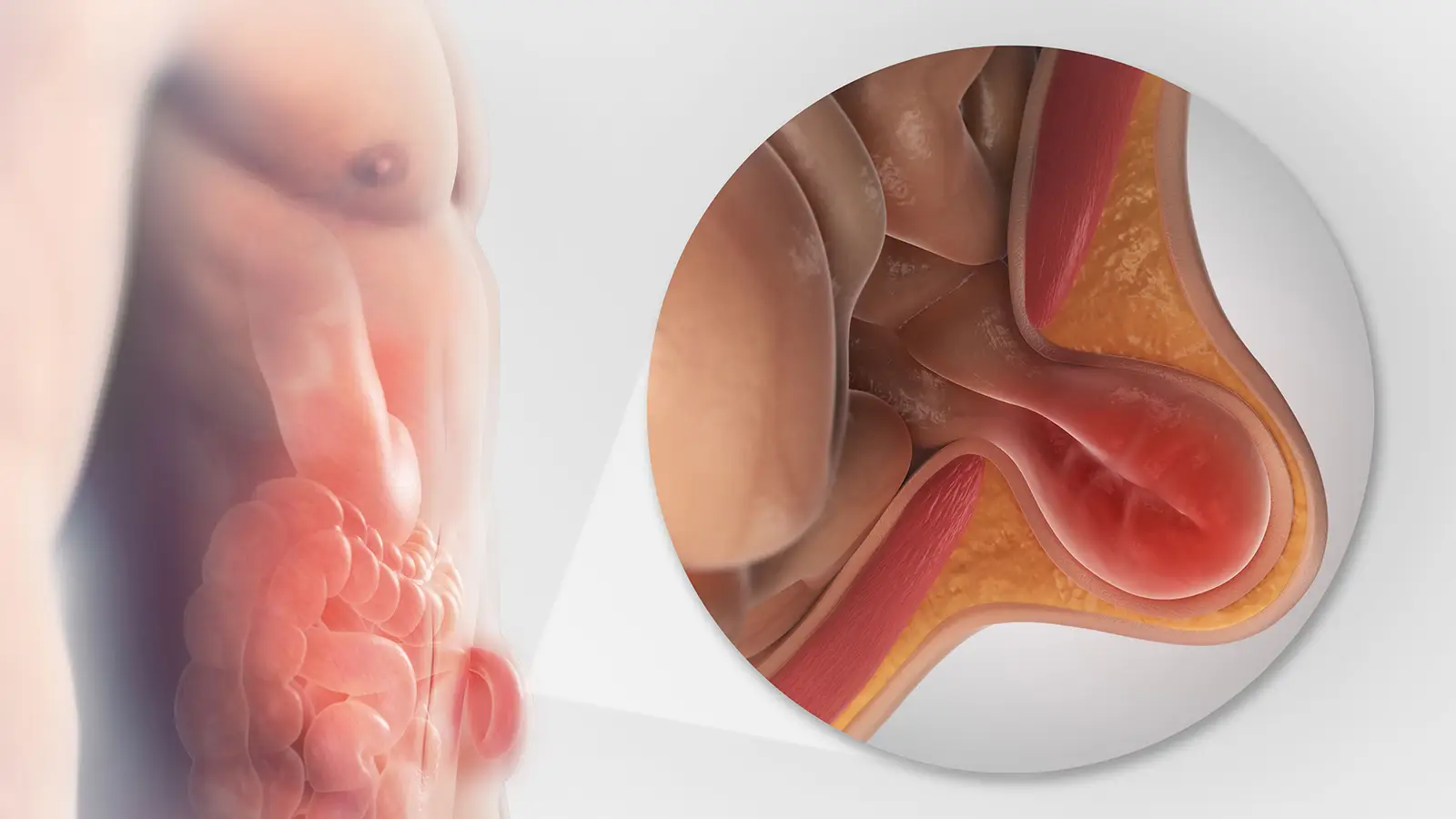

Types of Hernia
Causes
-
Obesity
-
Pregnancy
-
Increased physical exertion in the abdomen
-
coughing or sneezing frequently
-
lifting heavy or regular weights
-
Chronic Constipation
Symptoms of Kidney Stones
-
A small lump initially in the affected area
-
Pain or discomfort in the groin or abdomen while performing physical activities
-
Discomfort while sneezing or coughing
-
Constipation
-
Discomfort while walking, sitting down
-
Pain and burning sensations in the groin or abdominal region
-
Disappearance or reduction in the size of the lump while lying down
Grades
Grade I
Formation of a Lump Visible to the naked eye
Generally, in the first stage, a person might experience a lump or swelling in and around the areas of the abdomen. The lump will be clearly visible while straining, coughing, and carrying out other physical activities but the same lump might disappear or get reduced as soon as the person lies down. Initially, the person would not feel any sort of pain or discomfort.
Grade II
Obstruction
Gradually, the loop of the intestine becomes trapped, making one to lose the ability to make the bulge flat, which can lead to many complications and can also involve discomfort and severe pain. Such cases can worsen over time and may require immediate medical attention. Usually, it is a bad idea to leave it untreated as it can cause further swelling of the loop and eventual strangulation of the tissue or intestine which can be life-threatening.
Grade III
Stangulation
If the hernia resists manual pressure and can’t be popped back through the abdominal wall, it is called a non-reducible hernia or strangulated hernia. At this stage, it blocks the muscle tissue from inside, stopping blood circulation in the small intestine leading to infections in the dead cells. There may be signs like blood in stools, acute pain in the abdomen, fatigue, fever, nausea, vomiting and constant fever in case of a strangulated hernia.
When to consult a doctor ?
Treatment Options & Cost
There are certain non-surgical treatment options for treating hernia such as medication and lifestyle changes. If a person is not fit for the surgery is awaiting a surgery , they might be able to ease the pain or discomfort for some time by wearing a corset, binder, or truss. However, these are temporary solutions as a hernia usually does not go away on its own without surgery.
Undergoing a hernia repair surgery is the only treatment to permanently repair a hernia. If the hernia does not cause any pain or discomfort, the doctor may recommend a watchful waiting and continue observing the hernia until the patient is ready to undergo a surgery. In most cases, doctors recommend surgical repair of the hernia to prevent potential complications that can be life-threatening.
1) Open Hernia Repair Surgery – It is the conventional and most commonly performed surgery for hernia repair around the globe. In an open surgery for hernia repair, the surgeon makes an incision or a cut in the groin after which the hernia “sac” containing the bulging intestine is identified. He then pushes the hernia back into the abdomen and closes the abdominal wall with stitches. In case the opening is large, the surgeon may use a synthetic mesh to strengthen the closure through which the hernia protrudes.
2) Laparoscopic Hernia Repair Surgery – It is a much-advanced procedure for inguinal hernia treatment. Laparoscopic hernia repair surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery is the surgical procedure performed through tiny incisions instead of a large opening. The surgeon will make minute incisions depending upon the severity of the hernia, through which a thin laparoscope with a camera attached to it is inserted and the abdomen is inflated with a harmless gas (CO2), creating space for the surgeon to view the internal structures. The surgeon might use a synthetic mesh to strengthen the abdominal wall. After the procedure is completed, the small abdominal incisions are closed and within a month, they are barely visible. Doctors don’t recommend this procedure of hernia repair for children and pregnant women.
As with most surgeries, preparation for hernia surgery will involve restrictions in terms of diet. To ensure a safe treatment, one will be asked to refrain from drinking water, food, or any other fluids for six hours prior to the treatment as food present within the digestive system might lead to certain complications during the surgery.
While some drugs might be prescribed to be taken beforehand to aid the surgery, a certain number of drugs should be avoided for up to a week before the surgery because of the various effects they can have over the body.
Drugs like aspirin, blood thinners, anti-inflammatory medications (arthritis medications) and Vitamin E should be avoided prior to a week before the surgery.
Preoperative preparations include medical evaluations such as blood tests, chest x-rays and electrocardiography tests depending on the person’s age and medical condition.
It is recommended to take a shower before going for the operation as the surgical area must be kept dry after the operation.
The patient will be given a general anaesthesia so that the patient does not feel any sort of pain or discomfort during the surgery.
Depending upon the severity of the given condition, small incisions will be made around the affected area, which will help the surgeon to push back the hernia inside.
Through one of the incisions, the surgeon inserts a laparoscope which is a medical device having an inbuilt camera which enables them to view the internal structures.
A surgical mesh is inserted through the incision which supports the damaged tissue around the hernia as it heals.
After placing the mesh over the open hernia, the surgeon uses additional medical devices such as tacks, sutures, and surgical glue to hold the surgical mesh in its place.
The small incisions are then closed with stitches or sutures that dissolve on their own over time.
It is advised to avoid lifting anything that can make one strain and exert physical pressure for a particular time duration as it can lead the hernia to reoccur and can also invite certain other complications post the surgery.
It is important to maintain a diet which includes a good amount of fibre and fluids after a hernia surgery to not have constipation. Obe must follow the diet prescribed by the doctor.
The surgical area must be kept dry and clean for at least 48 hours and even if one takes a shower, the area surrounding the surgery should be patted dry to avoid any infection.
One should be hydrated and drink as much water as possible to avoid complications like constipation or straining during bowel movements.
The cost of a laparoscopic hernia surgery may vary depending on various factors such as the type of hernia, severity of the condition and hospitalization. The cost of a laparoscopic hernia repair surgery may vary between Rs 65,000 to Rs 1,25,000. To find out about a hernia surgery cost for yourself, you may contact the medical assistance team of a particular Surgical Sathi clinic or hospital.
The intestine or the protruding tissues through the abdominal wall are pushed back and a surgical mesh is placed around the damaged tissue. Over a period of time, the hernia will heal itself. However, to prevent the recurrence of hernia, it is extremely important to avoid physically stressful activities and take adequate precaution to get the most effective results.
Insurance Coverage
One thing you should know is that medical treatment for hernia won’t be covered in the insurance policy. Only the expenses of surgical treatment are covered and you also need to be hospitalized for at least 24 hours to file for a claim. You can opt for cashless payment or get reimbursement claims from your insurance providers as well.
If your claim is approved, you will be able to cover the entire cost of treatment, including diagnostic tests, medications, hospital stay, bed charges, and other consumables. Some of the best and most popular healthcare insurance providers are Oriental, Religare Health, Manipal Cigna, United India Insurance, Care Health, New India Insurance, Star Health & Allied, Bajaj Allianz General Insurance, ICICIA Lombard, Max Bupa Health Insurance.
Recovery Rate
Surgical repair possibilities come in two different categories. Recovery from open hernia surgery, in which the surgeon makes a lengthy incision to force the protruding organ back into place, typically takes at least three weeks. In the case of a laparoscopic hernia repair, recuperation takes one to two weeks.
Post discharge instructions recieved in the discharge summary and advise from the Operating surgeon is to be followed for complete recovery.
