Advanced Laser Deep Vein Thrombosis
Deep Vein Thrombosis?
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis?
How does it form?
Types of disease
Causes
-
Hereditary
-
Obesity
-
Injury
-
Prolonged sitting or standing
-
Cancer
-
Birth control pills
-
Prolonged bed rest
-
Smoking
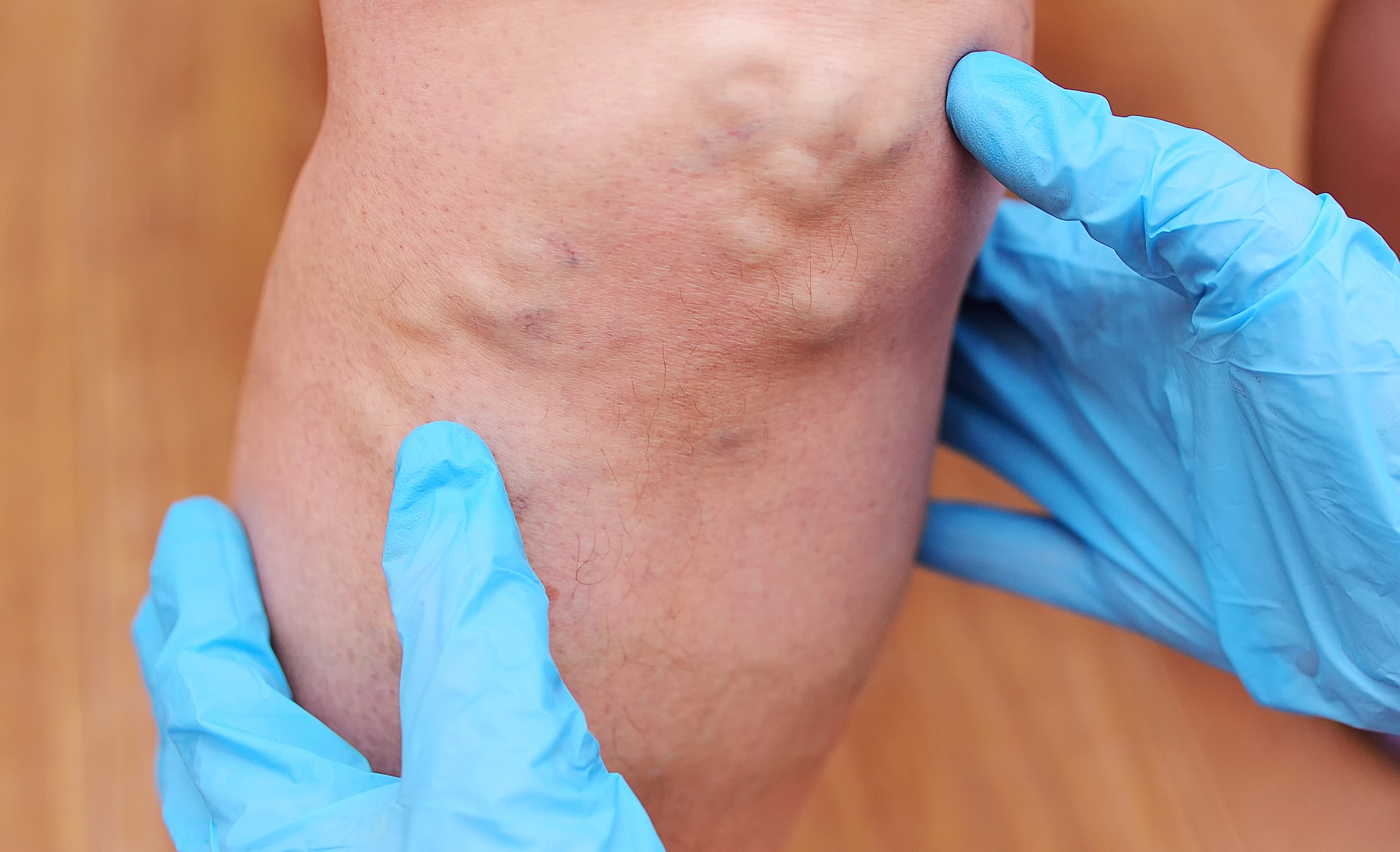

Symptoms
-
Swelling on the calf of one or both the legs
-
Pain that may worsen due to prolonged standing or walking
-
Red or discoloured skin on the legs followed by a warm sensation
-
Veins that are swollen, red, hard and appear tender while touching
-
Cramping pain in the affected leg that usually initiates in the calf
-
Shoulder pain
-
Neck pain
-
Swelling in the arm or hand
-
Blue tinted skin colour
-
Pain that moves from the arm to the forearm
-
Feeling of weakness in the hand
-
Coughing that may bring up blood
-
Sharp pain in or tightening in the chest
-
Pain in the shoulder, arm, back, or jaw
-
Shortness of breath or rapid breathing
Grades
Grade I
Normal Blood Flow
At this stage, the blood is flowing freely and mixing with the blood’s natural anticoagulants, which prevent blood cells from clotting.
Grade II
Coagulation
This process, which is also referred to as clotting, occurs when blood transitions from a liquid condition to a gel, causing a thrombus or blood clot to develop. Blood clots can occur for a variety of reasons, including smoking, obesity, injury, extended sitting, standing, or lying down, pregnancy, etc.
Grade III
Venous Thrombosis
The blood clot starts to form at this point in the deep veins, commonly in the legs. In this stage, the patient may exhibit particular symptoms like swelling and leg pain. Even while a venous thrombosis may not be dangerous right away, it might eventually cause a blood clot in the lungs if a piece of the thrombus breaks off and flows towards the lungs.
Grade IV
Pulmonary Embolism
The blood clot becomes trapped in the pulmonary artery at this stage, restricting or interrupting blood flow to the lungs. A pulmonary embolism can have serious complications that may be life-threatening if it is not treated right away.
Risks & Complications
During the surgery
Reaction to the anaesthesia
Excessive bleeding
Infection
Blood clots
Damage to blood vessels
Stroke
After the surgery
Postphlebitic/Post-thrombotic Syndrome: Chronic pain, swelling, skin discoloration, skin sores, and other symptoms in the leg are all signs and symptoms of a chronic venous insufficiency that develops after deep vein thrombosis surgery. This condition is known as postphlebitic/post-thrombotic syndrome.
If left untreated
If a condition of venous insufficiency like DVT is left untreated, it can lead to complications that can be severe and life threatening. In case you don’t seek proper treatment for DVT on time, the blood clot can travel to the lungs from other parts of the body, blocking one or more arteries or blood vessels in your lungs, resulting in a fatal complication of pulmonary embolism. A pulmonary embolism is followed by a number of signs and symptoms that include shortness of breath, chest pain while coughing or inhaling, a rapid heart rate, etc..
When to consult a doctor ?
Swelling, pain, and skin discoloration are just a few of the indications and symptoms of DVT. If you have any of these, you should see a doctor right once to begin treatment.
A pulmonary embolism has developed if you have signs and symptoms such sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, rapid heartbeat, coughing up blood, or disorientation. A pulmonary embolism can lead to complications that are immediately life-threatening, making it a medical emergency.
Treatment Options & Cost
The problem of deep vein thrombosis can be treated non-invasively by preventing the blood clot from growing or escaping and travelling to the lungs. The doctor may recommend a variety of drugs or preventive tools depending on the severity of your disease, including:
Blood thinners: Also referred to as anticoagulants, blood thinners are frequently used to treat DVT. In spite of the fact that these medications do not definitely dissolve blood clots, they can stop them from growing larger and lower your chance of getting new clots.
Compression stockings: To lessen the likelihood of forming blood clots and pools, you might think about using compression stockings. The use of these stockings can aid to reduce swelling and offer momentary comfort to thesymptoms brought on by a DVT problem.
Thrombolytics/Clot-busters are specific medications that a doctor could prescribe to dissolve blood clots that have developed in the vessels. These are typically administered if the other treatments are not working for you or if you have a more severe case of DVT that has resulted in pulmonary embolism.
Numerous surgical or less invasive techniques are available to treat blood clots or the DVT condition. If the drugs are unable to improve your condition, the doctor will typically suggest surgery. Deep vein thrombosis conditions are often treated using a combination of one or more of the following techniques:
Thrombolysis
Thrombectomy
Stenting and angioplasty
the deep vein being fitted with a vena cava filter
medicines that prevent clotting
IVC Filter: This is a metallic device inserted inside the inferior vena cava, which is a vein that travels through the abdomen. IVC filters work to stop blood clots from reaching the lungs thus lowering the risk of pulmonary embolism. An abdominal incision is created during the surgery, and an X-ray-guided catheter is placed into the vein. The filter is then placed over the blood clot inside the vein, where it eventually becomes anchored to the vein’s walls. In the event that you are unable to take blood-thinning medications, this course of treatment is typically recommended.
Catheter-directed thrombolysis: This minimally invasive therapy dissolves the aberrant blood clots that are already present in the blood vessels to aid in improving blood flow and stop any further harm to the tissues and organs. The medical gadget is applied to the site of a blood clot using catheter-directed thrombolysis, which is guided by X-ray imaging. This helps to dissolve the obstruction.
Acute iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis is a condition that is typically treated by percutaneous mechanical thrombectomy/Angioplasty, which is regarded as being very safe and successful. Combining a percutaneous thrombectomy with percutaneous transluminal angioplasty entails inserting a catheter with an inflating balloon through a very small incision near the clot. After being injected, the balloon is inflated and gradually drawn back outside, completely dislodging the clot from the vein.
Open thrombectomy: Also known as venous thrombectomy, this is a procedure that involves a surgical removal of the blood clot present inside an artery or a vein. During this procedure, the surgeon makes cuts or incisions in the blood vessels around the blood clot. Once the blood clot is identified, the surgeon removes the blood clot before repairing the blood vessels and the tissues.Open thrombectomy, sometimes referred to as venous thrombectomy, is a surgical operation that removes a blood clot from an artery or vein. The surgeon makes slits or incisions in the blood arteries surrounding the blood clot during this surgery. After locating the blood clot, the surgeon removes it before mending the tissues and blood arteries.
Before going for a deep vein thrombosis operation, it is crucial for you to discuss any prescribed or over-the-counter medications you are taking, such as aspirin, vitamins, blood thinners and other supplements.
It is generally a good idea to go over the symptoms and indicators with your surgeon before the procedure. This aids in excluding any potential issues that might emerge during treatment.
Smoking must be fully avoided as it may cause the healing process following surgery to be delayed.
You should let your doctor know if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant before receiving therapy.
You should inform your doctor of any potential allergic reactions because the operation calls for the injection of anaesthetic.
So as to make sure It is a safe and successful procedure, but you must fast for eight hours prior to the operation.
On the day of surgery, the doctor may physically examine your condition and carry out certain medical tests such as ultrasound, venogram, arteriogram, CT scan, MRI scan and blood tests
To make sure that you do not feel any sort of pain or discomfort during the surgery, the surgeon will sedate you with anaesthesia.
While performing the surgery, the doctor may use continuous X-ray images to view your internal structures.
The surgeon will make a cut or incision in the area above the blood clot that will help them to open the blood vessel and take out the clot.
A balloon attached to a catheter will be used in the blood vessel to remove any part of the clot that remains and a stent might be put in the blood vessel to keep it open during the procedure.
After the blood flow is restored, the doctor will cose and repair the blood vessel.
Once the procedure is complete, the surgeon will close the incision with stitches or sutures before applying bandages around the wound.
You will be kept in a recovery room until the effects of the anaesthetic wear off after the blood clot is removed and the surgery is finished.
Your vital signs, including your breathing and heart rate, will be observed by the medical staff.
You will be transferred to a ward or hospital room as soon as you are fully awake.
You will be ready for a hospital discharge based on your general health status.
Deep vein thrombosis therapy outcomes typically take time to manifest. To achieve the best outcomes possible during the entire healing process, it is crucial to strictly adhere to the doctor’s instructions and prescribed medications. To ensure a proper and thorough recovery, it is also advised to keep all follow-up appointments with the doctor.
An operation to treat deep vein thrombosis might cost anything from Rs. 1,70,000 to Rs. 2,50,000. This price shouldn’t be taken as an absolute because it can change depending on the severity of the ailment, the hospitalisation fee, and the doctor’s fees based on their specialisation. Contact the medical help staff of any specific Surgical Sathi facility or hospital to learn the exact price of a deep vein thrombosis operation for you.
Insurance Coverage
Recovery Rate
Deep vein thrombosis surgery recovery rates vary from patient to patient based on a range of variables including the severity of the condition, postoperative precautions, carefully adhering to the doctor’s instructions, and the patient’s body’s response to the procedure.
In most situations, deep vein thrombosis-related discomfort and swelling starts to subside within a few days of treatment, and you can return to your normal routine one week after surgery. However, a post-thrombotic syndrome may occasionally manifest along with symptoms including pain, edoema, and skin discoloration surrounding the affected location.
